Understanding Coagulation Disorders in Infants: A Comprehensive Guide
Coagulation disorders in infants represent a serious health concern that parents should be vigilant about. This condition occurs when a child’s body struggles to clot blood effectively, potentially leading to prolonged bleeding and severe complications if not treated properly. In this article, we will explore the causes, symptoms, and treatment options available for these disorders, helping parents take proactive measures in their child’s healthcare.
Coagulation disorders in infants can lead to serious health issues if not detected early.
What Are Coagulation Disorders?
Coagulation is the body’s response mechanism that starts immediately after an injury, where platelets form a plug at the site to stop the bleeding, reinforced by fibrin strands. However, when an infant has a coagulation disorder, bleeding can continue without cessation, leading to internal bleeding, particularly in joints and muscles.
In the infant body, coagulation factors are proteins produced through genetic mechanisms, essential for forming clots to prevent excessive bleeding. These factors must be balanced, as too little can lead to uncontrolled bleeding, while too much can cause thrombosis.
A coagulation disorder is identified when platelet counts drop below 150,000 μL, with spontaneous bleeding occurring when counts fall below 20,000 μL. Without timely intervention, the disorder can result in severe complications such as joint hemorrhages, cerebral bleeding, and even sepsis.
Causes of Coagulation Disorders in Infants
Genetic Factors
Coagulation disorders can stem from genetic disorders that affect the development of coagulation factors in the womb. The inheritance risk from parents can be as high as 50%, with males being more likely to be affected than females. Disorders such as hemophilia are prevalent, posing significant risks.
Genetic Mutations
Mutations can prevent sufficient production of crucial factors like VIII and IX required for clotting, which can arise even in fetuses, often without any family history of such diseases.
Vitamin K Deficiency
Vitamin K plays a vital role in blood coagulation. Infants may develop deficiencies due to lack of dietary intake, underdeveloped gut bacteria, or maternal anticoagulant medication. This deficiency can lead to life-threatening internal bleeding in infants.

Vitamin K deficiency can lead to coagulation disorders in infants.
Other Health Conditions
Coagulation disorders can also result from liver disease, severe infections, or immune system dysfunction, making it crucial to monitor an infant’s overall health.
Common Types of Coagulation Disorders
-
Hemophilia: A hereditary condition where blood doesn’t clot properly due to inadequate clotting factors. It mainly affects boys.
-
von Willebrand Disease: Caused by a deficiency or dysfunction of von Willebrand factor, important for platelet aggregation.
-
Vitamin K Deficiency Bleeding (VKDB): Occurs in newborns lacking sufficient vitamin K, leading to bleeding in crucial areas, including the brain.
-
Thrombocytopenia: A low platelet count can be caused by various factors including genetic conditions and certain medications.
- Microangiopathic Hemolytic Anemia (TMA): A group of disorders leading to the destruction of red blood cells due to small blood clots.
The Dangers of Coagulation Disorders
Without prompt treatment, coagulation disorders can have life-threatening consequences. Severe bleeding, particularly in critical areas such as the brain, can result in permanent damage or death. During pregnancy, these disorders can lead to complications like miscarriage or stillbirth, affecting both mother and child.
Recognizing Symptoms in Infants
Parents should be aware of the following symptoms of coagulation disorders:
- Abnormal Bleeding: Prolonged bleeding from minor cuts or after procedures like circumcision.
- Easy Bruising: Unexplained bruises appearing on the skin.
- Pale or Cyanotic Skin: Signs of reduced blood flow or blood loss.
- Swelling in Joints or Muscles: Indicative of internal bleeding.
- Intracranial Bleeding: Symptoms such as seizures, difficulty breathing, or lethargy.
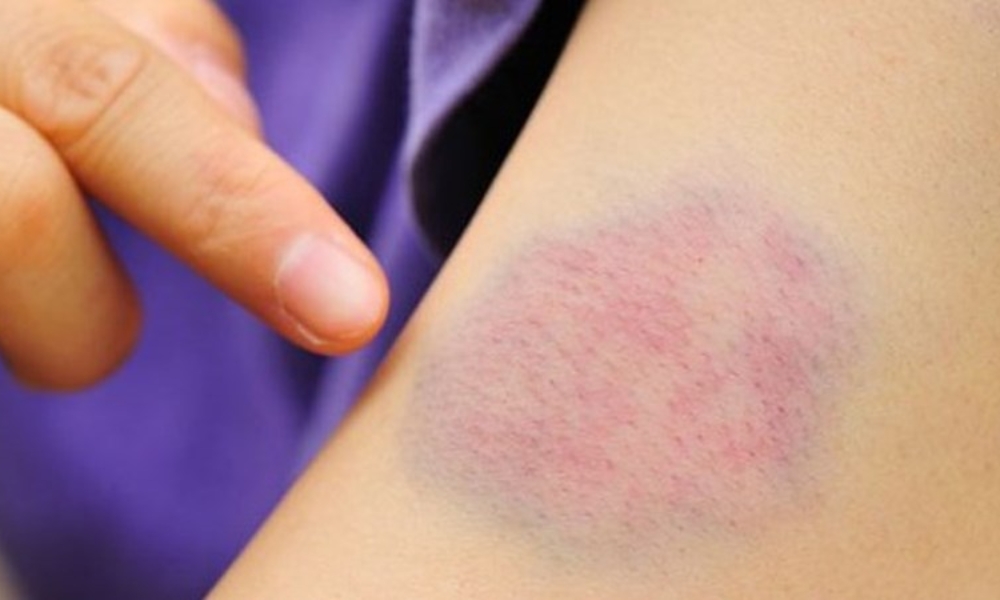
Infants with coagulation disorders may bruise easily.
Diagnostic Methods for Coagulation Disorders
Blood tests are essential for diagnosing coagulation disorders. Key tests include:
- Complete Blood Count (CBC): Analyzes the number of red blood cells and platelets.
- D-dimer Test: Determines the presence of clot degradation products.
- PT-INR Test: Measures the time it takes for blood to clot and assesses factor deficiencies.
- Genetic Testing: Identifies mutations causing coagulation abnormalities.
Treatment for Coagulation Disorders in Infants
Timely treatment is crucial for managing coagulation disorders:
- Vitamin K Supplementation: Administered immediately after birth to prevent VKDB.
- Replacement Therapy: For genetic disorders like hemophilia, this involves providing the missing clotting factors via injections.
- Management of Underlying Conditions: Treating infections or liver disease contributing to the disorder.
- Supportive Care: Close monitoring and provision of necessary medical care to ensure recovery.
Proper care and attention can significantly improve outcomes for infants with coagulation disorders.
Conclusion
Coagulation disorders in infants are serious medical conditions that require early detection and treatment. Parents should be vigilant in monitoring their child’s health and consult healthcare professionals when any symptoms arise. By following medical guidance and ensuring appropriate interventions, the risks associated with coagulation disorders can be significantly reduced.
For more information on content sharing in various formats, check out Sharing a video on TikTok – How to make it easily?.
Further Reading
- 3 Ways to Recover, Retrieve Deleted Videos On TikTok
- TikTok will allow users to upload videos up to 10 minutes long
- How To Set TikTok Password extremely fast, simple, and detailed
By understanding coagulation disorders better, parents can navigate the challenges of this condition more effectively, ensuring their child’s health and safety.
Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.